几个反三角函数的图形,其中,反余切以复变分析定义,因此在原点处出现不连续断点
在数学中,反三角函数(英语:inverse trigonometric function)是三角函数的反函数。
符号 等常用于
等常用于 等。但是这种符号有时在
等。但是这种符号有时在 和
和 之间易造成混淆。
之间易造成混淆。
在编程中,函数 ,
,  ,
,  通常叫做
通常叫做 ,
,  ,
,  。很多编程语言提供两自变量atan2函数,它计算给定
。很多编程语言提供两自变量atan2函数,它计算给定 和
和 的
的 的反正切,但是值域为
的反正切,但是值域为![{\displaystyle [-\pi ,\pi ]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/cb064fd6c55820cfa660eabeeda0f6e3c4935ae6) 。
。
-
在笛卡尔平面上

(红)和

(绿)函数的常用主值的图像。
-
在笛卡尔平面上

(红)和

(绿)函数的常用主值的图像。
-
在笛卡尔平面上

(红)和

(绿)函数的常用主值的图像。
下表列出基本的反三角函数。
| 名称
|
常用符号
|
定义
|
定义域
|
值域
|
| 反正弦 |
 |
 |
![{\displaystyle [-1,1]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/51e3b7f14a6f70e614728c583409a0b9a8b9de01) |
![{\displaystyle [-{\frac {\pi }{2}},{\frac {\pi }{2}}]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9dc480741da18128936a24486e90845e818ee6ff)
|
| 反余弦 |
 |
 |
![{\displaystyle [-1,1]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/51e3b7f14a6f70e614728c583409a0b9a8b9de01) |
![{\displaystyle [0,\pi ]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3e2a912eda6ef1afe46a81b518fe9da64a832751)
|
| 反正切 |
 |
 |
 |

|
| 反余切 |
 |
 |
 |

|
| 反正割 |
 |
 |
![{\displaystyle (-\infty ,-1]\cup [1,+\infty )}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/5dedf8ddf2dcc93b2f0799dfd206f0064a74e94f) |
![{\displaystyle [0,{\frac {\pi }{2}})\cup ({\frac {\pi }{2}},\pi ]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/37a9f637f021269e58fee9ea489e699fa4a9c817)
|
| 反余割 |
 |
 |
![{\displaystyle (-\infty ,-1]\cup [1,+\infty )}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/5dedf8ddf2dcc93b2f0799dfd206f0064a74e94f) |
![{\displaystyle [-{\frac {\pi }{2}},0)\cup (0,{\frac {\pi }{2}}]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/959c8fba2c5bd4a90ecbfb9b2aef71e170c755d6)
|
(注意:某些数学教科书的作者将 的值域定为
的值域定为 因为当
因为当 的定义域落在此区间时,
的定义域落在此区间时, 的值域
的值域 ,如果
,如果 的值域仍定为
的值域仍定为![{\displaystyle [0,{\frac {\pi }{2}})\cup ({\frac {\pi }{2}},\pi ]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/37a9f637f021269e58fee9ea489e699fa4a9c817) ,将会造成
,将会造成 ,如果希望
,如果希望 ,那就必须将
,那就必须将 的值域定为
的值域定为 ,基于类似的理由
,基于类似的理由 的值域定为
的值域定为![{\displaystyle (-\pi ,-{\frac {\pi }{2}}]\cup (0,{\frac {\pi }{2}}]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2f6678056315765524d454508602d40af100c818) )
)
如果 允许是复数,则
允许是复数,则 的值域只适用它的实部。
的值域只适用它的实部。
余角:



负数参数:






倒数参数:












如果有一段正弦表:



注意只要在使用了复数的平方根的时候,我们选择正实部的平方根(或者正虚部,如果是负实数的平方根的话)。
从半角公式 ,可得到:
,可得到:




通过定义可知:

|

|

|

|
图示
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
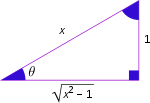
|
每个三角函数都周期于它的参数的实部上,在每个 区间内通过它的所有值两次。正弦和余割的周期开始于
区间内通过它的所有值两次。正弦和余割的周期开始于 结束于
结束于 (这里的
(这里的 是一个整数),在
是一个整数),在 到
到 上倒过来。余弦和正割的周期开始于
上倒过来。余弦和正割的周期开始于 结束于
结束于 ,在
,在 到
到 上倒过来。正切的周期开始于
上倒过来。正切的周期开始于 结束于
结束于 ,接着(向前)在
,接着(向前)在 到
到 上重复。余切的周期开始于
上重复。余切的周期开始于 结束于
结束于 ,接着(向前)在
,接着(向前)在 到
到 上重复。
上重复。
这个周期性反应在一般反函数上:






对于实数 的反三角函数的导函数如下:
的反三角函数的导函数如下:

举例说明,设 ,得到:
,得到:

因为要使根号内部恒为正,所以在条件加上 ,其他导数公式同理可证[1]。
,其他导数公式同理可证[1]。
积分其导数并固定在一点上的值给出反三角函数作为定积分的表达式:

当 等于1时,在有极限的域上的积分是瑕积分,但仍是良好定义的。
等于1时,在有极限的域上的积分是瑕积分,但仍是良好定义的。
如同正弦和余弦函数,反三角函数可以使用无穷级数计算如下:
![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\arcsin z&{}=z+\left({\frac {1}{2}}\right){\frac {z^{3}}{3}}+\left({\frac {1\cdot 3}{2\cdot 4}}\right){\frac {z^{5}}{5}}+\left({\frac {1\cdot 3\cdot 5}{2\cdot 4\cdot 6}}\right){\frac {z^{7}}{7}}+\cdots \\&{}=\sum _{n=0}^{\infty }\left[{\frac {(2n)!}{2^{2n}(n!)^{2}}}\right]{\frac {z^{2n+1}}{(2n+1)}};\qquad |z|\leq 1\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c89d945076c1fce9d92ad559ec2130fa883c5bce)
![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\arccos z&{}={\frac {\pi }{2}}-\arcsin z\\&{}={\frac {\pi }{2}}-\left[z+\left({\frac {1}{2}}\right){\frac {z^{3}}{3}}+\left({\frac {1\cdot 3}{2\cdot 4}}\right){\frac {z^{5}}{5}}+\left({\frac {1\cdot 3\cdot 5}{2\cdot 4\cdot 6}}\right){\frac {z^{7}}{7}}+\cdots \right]\\&{}={\frac {\pi }{2}}-\sum _{n=0}^{\infty }\left[{\frac {(2n)!}{2^{2n}(n!)^{2}}}\right]{\frac {z^{2n+1}}{(2n+1)}};\qquad |z|\leq 1\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/31e176ffdceceb486b2bde9b798995e9544143fe)


![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\operatorname {arcsec} z&{}=\arccos \left(z^{-1}\right)\\&{}={\frac {\pi }{2}}-\left[z^{-1}+\left({\frac {1}{2}}\right){\frac {z^{-3}}{3}}+\left({\frac {1\cdot 3}{2\cdot 4}}\right){\frac {z^{-5}}{5}}+\left({\frac {1\cdot 3\cdot 5}{2\cdot 4\cdot 6}}\right){\frac {z^{-7}}{7}}+\cdots \right]\\&{}={\frac {\pi }{2}}-\sum _{n=0}^{\infty }\left[{\frac {(2n)!}{2^{2n}(n!)^{2}}}\right]{\frac {z^{-(2n+1)}}{(2n+1)}};\qquad \left|z\right|\geq -4\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d09d36851c528df3de9f33d85a376311d09057fc)
![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\operatorname {arccsc} z&{}=\arcsin \left(z^{-1}\right)\\&{}=z^{-1}+\left({\frac {1}{2}}\right){\frac {z^{-3}}{3}}+\left({\frac {1\cdot 3}{2\cdot 4}}\right){\frac {z^{-5}}{5}}+\left({\frac {1\cdot 3\cdot 5}{2\cdot 4\cdot 6}}\right){\frac {z^{-7}}{7}}+\cdots \\&{}=\sum _{n=0}^{\infty }\left[{\frac {(2n)!}{2^{2n}(n!)^{2}}}\right]{\frac {z^{-(2n+1)}}{2n+1}};\qquad \left|z\right|\geq 1\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7c4732b95840d2de49c0c3c48267cccad551991e)
欧拉发现了反正切的更有效的级数:
 。
。
(注意对 在和中的项是空积1。)
在和中的项是空积1。)

使用分部积分法和上面的简单导数很容易得出它们。
使用 ,设
,设

则

换元

则

且

换元回x得到





















- ^
设
 ,得到:
,得到:

因为要使根号内部恒为正,所以在条件加上 。
。
设 ,得到:
,得到:

设 ,得到:
,得到:

设 ,得到:
,得到:

因为要使根号内部恒为正,所以在条件加上 ,比较容易被忽略是
,比较容易被忽略是 产生的绝对值
产生的绝对值 的定义域是
的定义域是 ,所以
,所以 ,所以
,所以 要加绝对值。
要加绝对值。
设 ,得到:
,得到:

因为要使根号内部恒为正,所以在条件加上 ,比较容易被忽略是
,比较容易被忽略是 产生的绝对值
产生的绝对值 的定义域是
的定义域是 。
。
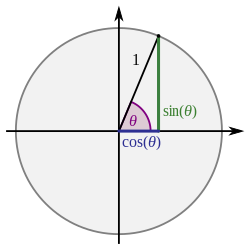




















![{\displaystyle [-\pi ,\pi ]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/cb064fd6c55820cfa660eabeeda0f6e3c4935ae6)











![{\displaystyle [-1,1]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/51e3b7f14a6f70e614728c583409a0b9a8b9de01)
![{\displaystyle [-{\frac {\pi }{2}},{\frac {\pi }{2}}]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9dc480741da18128936a24486e90845e818ee6ff)


![{\displaystyle [0,\pi ]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3e2a912eda6ef1afe46a81b518fe9da64a832751)









![{\displaystyle (-\infty ,-1]\cup [1,+\infty )}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/5dedf8ddf2dcc93b2f0799dfd206f0064a74e94f)
![{\displaystyle [0,{\frac {\pi }{2}})\cup ({\frac {\pi }{2}},\pi ]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/37a9f637f021269e58fee9ea489e699fa4a9c817)


![{\displaystyle [-{\frac {\pi }{2}},0)\cup (0,{\frac {\pi }{2}}]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/959c8fba2c5bd4a90ecbfb9b2aef71e170c755d6)







![{\displaystyle (-\pi ,-{\frac {\pi }{2}}]\cup (0,{\frac {\pi }{2}}]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2f6678056315765524d454508602d40af100c818)









































































![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\arcsin z&{}=z+\left({\frac {1}{2}}\right){\frac {z^{3}}{3}}+\left({\frac {1\cdot 3}{2\cdot 4}}\right){\frac {z^{5}}{5}}+\left({\frac {1\cdot 3\cdot 5}{2\cdot 4\cdot 6}}\right){\frac {z^{7}}{7}}+\cdots \\&{}=\sum _{n=0}^{\infty }\left[{\frac {(2n)!}{2^{2n}(n!)^{2}}}\right]{\frac {z^{2n+1}}{(2n+1)}};\qquad |z|\leq 1\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c89d945076c1fce9d92ad559ec2130fa883c5bce)
![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\arccos z&{}={\frac {\pi }{2}}-\arcsin z\\&{}={\frac {\pi }{2}}-\left[z+\left({\frac {1}{2}}\right){\frac {z^{3}}{3}}+\left({\frac {1\cdot 3}{2\cdot 4}}\right){\frac {z^{5}}{5}}+\left({\frac {1\cdot 3\cdot 5}{2\cdot 4\cdot 6}}\right){\frac {z^{7}}{7}}+\cdots \right]\\&{}={\frac {\pi }{2}}-\sum _{n=0}^{\infty }\left[{\frac {(2n)!}{2^{2n}(n!)^{2}}}\right]{\frac {z^{2n+1}}{(2n+1)}};\qquad |z|\leq 1\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/31e176ffdceceb486b2bde9b798995e9544143fe)


![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\operatorname {arcsec} z&{}=\arccos \left(z^{-1}\right)\\&{}={\frac {\pi }{2}}-\left[z^{-1}+\left({\frac {1}{2}}\right){\frac {z^{-3}}{3}}+\left({\frac {1\cdot 3}{2\cdot 4}}\right){\frac {z^{-5}}{5}}+\left({\frac {1\cdot 3\cdot 5}{2\cdot 4\cdot 6}}\right){\frac {z^{-7}}{7}}+\cdots \right]\\&{}={\frac {\pi }{2}}-\sum _{n=0}^{\infty }\left[{\frac {(2n)!}{2^{2n}(n!)^{2}}}\right]{\frac {z^{-(2n+1)}}{(2n+1)}};\qquad \left|z\right|\geq -4\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d09d36851c528df3de9f33d85a376311d09057fc)
![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}\operatorname {arccsc} z&{}=\arcsin \left(z^{-1}\right)\\&{}=z^{-1}+\left({\frac {1}{2}}\right){\frac {z^{-3}}{3}}+\left({\frac {1\cdot 3}{2\cdot 4}}\right){\frac {z^{-5}}{5}}+\left({\frac {1\cdot 3\cdot 5}{2\cdot 4\cdot 6}}\right){\frac {z^{-7}}{7}}+\cdots \\&{}=\sum _{n=0}^{\infty }\left[{\frac {(2n)!}{2^{2n}(n!)^{2}}}\right]{\frac {z^{-(2n+1)}}{2n+1}};\qquad \left|z\right|\geq 1\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7c4732b95840d2de49c0c3c48267cccad551991e)
















































